Everything in the world runs through some rules or governing bodies. Institutions, offices, and organizations run through code of conduct policies, etc. However, to keep a tab on the actions of such institutions, a separate structure exists. They advocate about the rights and wrongs in society. For example, Journalism equates to the fourth pillar in democracy. They show the public the true face of a situation, call out malpractices, and give the public a platform to make decisions through their unbiased reporting. Similarly, the United Nations and other non-profit organizations shed light on various issues present in the world. And drives awareness programs and campaigns that take a step towards changing society, that too for the better.
Aren’t you familiar with organizations that work towards the overall quality of life, human rights, world economy, and such? It would be of no surprise that apart from local governing bodies, an international structure exists that works closely with different countries to improve the existing situations and grow collectively. As mentioned above, the United Nations(UN) is an effort of all the world governments to tackle the indifferences in society, promote world peace, and resolve conflicts. Moreover, they have various subsidiaries that tackle diverse issues like- poverty, human trafficking, human rights, and so on.

ILO(International Labor Organization) is one such organization that falls under the subsidiary of the United Nations. ILO works toward upholding the human rights of working people. And set regulations to conserve justice and equality(through international labor laws). We explained just a brief outline of what ILO is. In reality, ILO covers a broader area in terms of its program outreach. So, What is ILO? Is India part of ILO? What is the purpose of ILO? Such questions will get answered in our blog. Keep on reading to understand International Labor Organization and everything you need to know about it.
Table of Contents
What is ILO(International Labor Organization)?
We all know the United Nations is the collective effort of governments to maintain peace, social justice, equality, and cordial relations. But apart from the UN, there are self-governed bodies that work closely with them. The main motive is to uphold the objectives of the UN, as stated above. These self-governed bodies may have a separate origin and yet be counted as a part of the UN agency to perform functions on its behalf.
ILO(International Labor Organization) is the oldest and the first autonomous bureau by the United Nations. Headquartered in Switzerland(Geneva), ILO works towards achieving a balanced and equal work environment. The organization ensures that people, regardless of any differences in race, gender, and other constructed norms, have access to secured, sustainable, and viable work.
ILO regulates the policies through International Labor Standards, which gives the people the right to set equal standards in the workplace. Moreover, the International Labor Standards aims at eliminating forced labor, child labor, and workplace discrimination of all sorts. The organization consists of 187 members and a staff of 2700 people(from around the world) to coordinate programs and projects. Read our blog “ILO: An easy Guide in 10 minutes ” to know more about ILO.
SUMMARY:
ILO is the oldest and the first autonomous bureau of the UN. It’s headquarter is in Geneva. The aim of ILO is to eliminate forced labor, child labor, and workplace discrimination of all sorts.
History of ILO

The origin of the 100-year-old International Labor Organization dates back to World War 1. The intention of reforming the social situation for the working class so that they don’t have to suffer the social inequalities as war took a lot on every sect of the society. Therefore, to protect the workforce interests and the union and end wage labor, the world powers suggested the inclusion of codes (of worker’s benefit) in the peace treaty (Versailles Peace Treaty). [Source- ILO]. Read our blog “ILO An easy Guide in 10 minutes ” to know more about ILO
The labor commission drafted the ILO in 1919, under the chairmanship of Samuel Gompers. The draft reflected concerted efforts of countries like- Cuba, the United States, Czechoslovakia, France, Italy, Japan, Poland, and the United Kingdom. Thus, on 11th April 1919, the first-ever and the oldest specialized office of the United Nations came into existence.
What Does ILO reflect? Mission of ILO
Every drafted commission has an agenda/motto they follow. The objectives define the road map of the activities, projects, programs, and scope of any. The ILO reflects the following ideas in its preamble:
- Social justice equates to universal peace. Meaning: universal peace and harmony exist when there is social justice.
- If there exist hardships, unrest, and injustice that indicate that world peace and harmony are at stake, immediate action is required.
- A nation that fails to adopt the proper working conditions of labor becomes a hindrance for nations seeking improvement in their respective countries.
Objectives of ILO
The objectives of International Labor Organization are as follows.
Promoting fundamental principles and right at work
Looking through the window of perspective, safeguarding fundamental rights is essential. It has nothing to do with the nature of work or the working itself. People irrespective of caste, creed, and gender deserve equal treatment.
Create decent work opportunities for both men and women with better employment and income
Job creation should think of both the gender participating in the welfare of the economy. The existence of job opportunities for both the gender, that too with decent remuneration and benefits, is essential for a developing economy. Pay, promotion, availability of jobs, and other such factors should be fair and square for both men and women.
Enhanced coverage and social protection for all

One can never be sure of what the future holds. Therefore, it is essential to have a backup plan for uncertainty in our lives, i.e., social coverage. Social protection covers factors such as- accessibility to healthcare, injury, maternity-related factors, sickness, unemployment, and death of the primary wage-earner. To ensure that maximum people are under the social coverage, ILO runs several programs and projects to make the vision of a safety net for all a reality. [Source- UN]. Read our blog “ILO easy Guide in 10 minutes ” to know more about ILO
Strengthen tripartism and dialogue
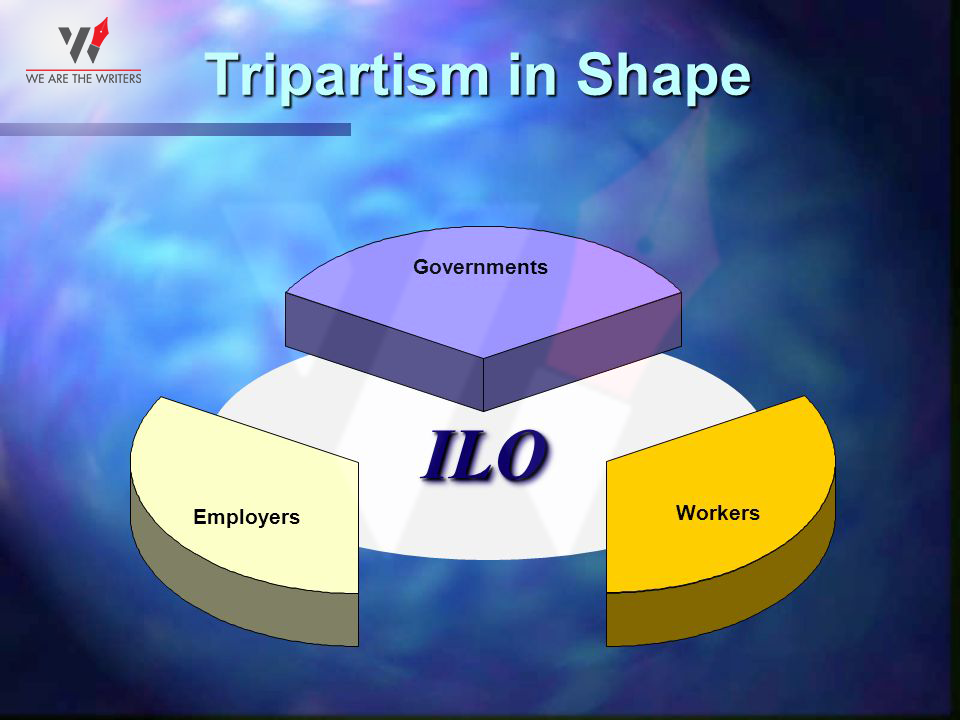
A well-conditioned environment that encourages active participation between employers, employees and government will foster social dialogue. It includes collective discussion, information exchange, negotiation, dispute prevention, conflict resolving, cooperation, etc. It is necessary to uphold these objectives to maintain a cooperative, sustainable, and progressive outlook towards work-related opportunities. The challenges must be met with a headstrong attitude and handled together.
Key Issues covered by ILO in Early Years
ILO moved to its present location, Geneva, in 1920. France’s Albert Thomas was its first director. The International Labor Organization addressed crucial factors to focus on for maintaining equality and fair practices in the workplace, which includes-
Work Hours: ILO Easy Guide in 10 minutes
Hours of Work Convention 1919 discusses the ideal work hours for the working people. The conditions in which the extension of working hours is acceptable. And undertaking of different industrial sectors.
Unemployment

The document discusses the measures taken to tackle unemployment in countries. It also collects the statistics regarding unemployment and presents them to the committee. It also promotes setting up free public employment agencies and other operations coordinated with ILO.
Maternity Protection
Maternity Protection Convention, 1919 proposes measures for situations such as women’s employment pre and post-childbirth and other related benefits.
Minimum Age
The convention of 1919 also discusses the minimum age limit to be employed. The age limit regulation lays a restriction on children under the age of 14 to work under any public or private organization. However, the convention of 1919 stated a lower age limit for child labor, i.e., 12 years.
Night Work of Young Persons
The Convention of 1919 discusses the employment of youth in the night time. It defines the work hours (11 hrs) and the break time for the night shift. The document also states exceptions for a few countries like Japan and India. Also, the convention mentions that the night shift can get canceled in the public interest.
Apart from the conventions and new changes, there exists a ‘Committee of Experts.’ The expert committee evaluates an unbiased report of the International Labor Standards of the member states of International Labor Organization.
Later on, the International Labor Organization became a global agency after it identified itself as an autonomous agency under the United Nations(1940).
Working Structure of the ILO
The ILO works as a multilayered organization- a tripartite organization, a one of its kind in the UN. It is essential to keep the government, worker’s unions, and employers in the loop. The balanced work agreement between these parties ensures sustainable development and opportunities without any bias. It is commendable to see that ILO takes its work division to such a detailed level that it covers all the intricacies and involvement.
Since ILO is a collective governmental organization, the governing body holds meetings from the regional level to its core level(UN).
Primary Bodies Present in the ILO
The tripartite structure of the ILO makes it very clear who the primary role-players of the organization are. Since the organization focuses on a sustainable and progressive working environment, it works closely with the government, workers’, and employers’ representatives.
International Labor Conference

The International Labor Conference, also addressed as the International Parliament of labor, is responsible for setting ILO policies and the International Labor Standard. It holds a meeting once a year for social discussion and the discussion of labor policies and questions.
The Governing Body

The governing body is the administrative panel of the organization. Before the policies get passed at the International Labor Conference, the governing body decides on the ILO policies. It also sets the program and its budget before it gets presented at the International Labor Conference. Moreover, the governing body meets three times a year at their headquarter (Geneva) to discuss policies.
International Labor Office
The International Labor Office is responsible for running the official activities under the supervision of the governing body. Also, the activities carried out under the leadership of the Director-General.
Regional Meetings
Such meetings happen periodically to address matters about a specific region to which the state members belong.
Is there any System that Overlooks the International Labor Standards at ILO?
There exists a supervisory system that upholds the policies framed by the International Labor Standards. The monitoring system is present at an international level. It works with a motive of observing the strategies laid out by the member state. The supervising unit points out the areas of improvement and makes sure that the member state implements them. Moreover, the supervising system assists the member state to the best of their abilities. The supervision standards follow two procedures to supervise the implementation of policies, which are:
A Regular System of Supervision
The regular system of supervision evaluates a recurrent report made by the member state and then determines whether the state members take the required measures to promote equal work opportunities or not.
Special Procedures
The special procedures have representatives to address the issue at hand. They also work by filing complaints if the member state fails at upholding the International Labor Standards.
Committee of Freedom of Association(CFA)
The parties (workers’ and employers’ organizations) can reach out to the Committee of Freedom of Association. The parties file a case with the CFA(Committee of Freedom of Association), which comprises a head person, representatives of the governments, employers, and workers. The situation gets evaluated and then receives proper guidelines from the governing body to correct the condition.
Surveys, Assistance & Training
Additionally, in-depth surveys help examine the implementation of the policies in the member state. The surveys get based on the data collected from the reports by employers’ and worker’s organizations. Assistance and training get provided in places where there is a need for a systematic procedure to address the issues.
Development Programs and Cooperation
ILO works closely with countries across the world to assist in the stages of economic development. Through its widespread country network and close partnership, the projects get carried out successfully. The projects get coordinated between the donors, receiving countries, and the International Labor Organization.
The development programs aim at creating a link that stands firm on the roles set by the International Labor Organization. The development of cooperation benefits people irrespective of their gender, race, and background. Also, it hands out feasible work opportunities for people, making the laid-out agendas of the International Labor Standards a reality.
Ever Since the beginning of the development programs in the 1950s, the International Labor Organization, with 600+ programs, impacted more than 100 countries. Such a feat is possible with the support from its 120 partners that support the cause.
Areas of Work
The missions and objectives set by the convention help the ILO to implement them accordingly. The following are a few of the areas that the ILO diligently works on:
Wages & Income
Wage is an essential part of any work, be it the public or private sector. You decide on your job based on your qualification and the aptitude for the job. Then, you receive the monetary benefit for the task you can skillfully complete. Ensuring minimum wage for survival is one of the areas of work of the International Labor Organization.
Collective Bargaining and Labor Relations

The purpose of collective bargaining is to negotiate the base wage, working conditions, and other demands. The worker’s union negotiates with the employer’s representatives and reaches on a neutral ground. Also, collective bargaining discusses justice, equal treatment, and safety. It helps the union raise a voice about rights and responsibilities, resulting in a productive work environment. Collective discussion increases productivity and minimizes differences.
Working time and the Work Organization
Humans are not machines. They need the energy to replenish themselves. Work, especially in the industrial areas, requires a lot of manual labor. To ascertain how many work hours are feasible for a human to work on without affecting their health remains a concern for the international labor governing body. Certain factors like- globalization, demographic changes, and global pandemic pose new challenges. The ILO mentions weekly rest and paid leaves to protect the rights of the employed people.
Non-Standard Form of Employment
Apart from the regular office schedule, there exists a non-standard form of employment. It does not happen permanently inside the work premises. The circumstances may include part-time work, self-employment, and temporary agency work.
Domestic Worker
Domestic workers are the house helps that assist with the chores. The work includes cooking, cleaning, attending to the sick, taking care of the pet, etc. Also, most household workers are women, while only a limited fraction comprises the male house workers(mostly gardeners or drivers). The part-time job does not let them have an employment agreement which leaves them vulnerable to exploitation. The ILO works toward protecting the rights of such workers and safeguarding their rights.
Employment Security
There may be times when there can be a steep slope in the working sphere. The reason for such a downfall is job loss. A person can lose a job under several circumstances like- poor performance, a terrible economic phase, crisis, company crisis, workforce cutting, etc. The Employment Protection Legislation safeguards the employees from such situations.
Crowdwork and the Gig Economy
Crowdwork and the gig economy comes under the non-standard form of employment. The digital labor platforms include services that are web-based and location-based. It is evident that with the shift of the world towards the digital sphere, there comes a need to understand such work profiles, especially for an organization like ILO. The research will help them understand the work structure of the gig economy. And devise appropriate policies around it.
Fighting Human Trafficking and Forced Labor

Human Trafficking is a serious issue that exists in our society. Many people get forced into doing labor and exploited physically and mentally. It affects everyone, from children to men and women. The exploitation, be it economic or sexual exploitation, concerns human as well as laborers’ rights. They need a strong voice that supports the said cause and protect them from such mishappening. To tackle such criminal injustice, the labor organization, the conventions, and the representatives must come together with other global organizations and create a safe space for everyone.
Forced labor and human trafficking fall into a close line, but they are a different issue altogether. However, there are most instances when victims of human trafficking end up doing forced labor. The number is pretty high. In a report by ILO, 12.3 million people have fallen into the hands of forced labor worldwide. Distinct policies should get made to protect the interest of victims of forced labor and trafficking.
ILO’s response to Covid
ILO, in all the sense, is directly related to work and policies around it worldwide. The global pandemic(Covid19/Coronavirus) took a toll on everyone, and jobs took a direct hit. This ordeal impacted the economy at large. To this day, people are still getting back on the tracks, returning to normal, and adjusting to the new normal.
To help the people and the less privileged section of the society, the ILO defines a four-pillar program that adheres to its objectives and protects the interests of people, businesses, etc. Country policy responses to Covid through the ‘Four Pillars of Action’ defined by the ILO.
- The first pillar talks of restoring jobs and the economy by providing monetary assistance to the health sector and other sectors. The efforts include devising policies that affect the economic aspect of the country.
- The second pillar discusses the policies that protect people from losing their jobs (job retention strategies). It supports businesses by providing tax exemption and stretches social protection for all.
- The third pillar aims at discussing policies that protect the workers in the work environment. The ILO targets worker’s safety by ensuring- adaptable work arrangements, safety measures at work, no work discrimination, access to healthcare, and extended paid leaves.
- The fourth pillar advises social dialogue between the government, employees, and employers. The active discussions will strengthen the dialogue between the three bodies to work collectively and address common challenges.
ILO in India
India shares a partnership with ILO that dates way back. India is a core member of the oldest autonomous organization since 1922. Its office in India got established in 1928. India adheres to ILO’s deep-rooted objective of providing decent work opportunities irrespective of race, creed, gender, or background. India pushes forward to develop and sustain the economy by providing equal opportunities to all and safeguarding worker’s rights.
India works through its priority program that focuses on three things
Priority 1: Skills development for everyone. The opportunities through skill development will open the doors of productivity for women and men, especially the youth.
Priority 2: Extending Social Protection.
Priority 3: Eliminating unacceptable work forms through active bargaining, discussion and dialogue, and equal participation.
ILO’s Agenda for 2030: Decent work and Sustainable Development

The ILO will be focusing on decent work, its core objective, and sustainable development as a part of the organization’s Agenda- 2030. The 2030 Agenda will focus on economic, social, and environmental stability. The organizations have 17 sustainable development goals, which will help them work actively towards a better world and handle challenges effectively.
Conclusion
By now, you must have gained information about what ILO is and how it helps the world governments. It is essential to have regulatory bodies to ensure no one in our society is left behind and has equal opportunities. Through ILO, it is evident that we are walking towards a society that will deny the social injustices and shape a better economy for all.





 WhatsApp
WhatsApp